Which Command Is Used To Determine The Route A Packet Takes?
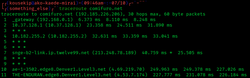 The traceroute control | |
| Original author(s) | Van Jacobson |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 1987 (1987) |
| Platform | Unix-like systems |
| Type | Control |
| Developer(s) | Microsoft, ReactOS Contributors |
|---|---|
| Platform | Windows, ReactOS |
| Type | Command |
| License | Microsoft Windows: Proprietary commercial software ReactOS: GNU General Public License |
In computing, traceroute and tracert are computer network diagnostic commands for displaying possible routes (paths) and measuring transit delays of packets across an Internet Protocol (IP) network. The history of the road is recorded as the round-trip times of the packets received from each successive host (remote node) in the route (path); the sum of the mean times in each hop is a measure of the full time spent to establish the connection. Traceroute proceeds unless all (usually three) sent packets are lost more than than twice; so the connection is lost and the route cannot be evaluated. Ping, on the other hand, only computes the final round-trip times from the destination point.
For Internet Protocol Version vi (IPv6) the tool sometimes has the name traceroute6 [ane] and tracert6 .[two]
Implementations [edit]
The command traceroute is available on many modernistic operating systems. On Unix-like systems such as FreeBSD, macOS, and Linux it is available as a command line tool. Traceroute is also graphically accessible in macOS within the Network Utilities suite.
Microsoft Windows and ReactOS provide a program named tracert that performs the same route-tracing role. Windows NT-based operating systems also provide PathPing, with similar functionality. The ReactOS version was adult past Ged Murphy and is licensed under the GPL.[3]
On Unix-like operating systems, traceroute sends, by default, a sequence of User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets, with destination port numbers ranging from 33434 to 33534; the implementations of traceroute shipped with Linux,[4] FreeBSD,[five] NetBSD,[6] OpenBSD,[7] DragonFly BSD,[eight] and macOS include an option to use ICMP Echo Request packets (-I), or whatsoever arbitrary protocol (-P) such every bit UDP, TCP using TCP SYN packets, or ICMP.[9]
On Windows, tracert sends ICMP Echo Request packets, rather than the UDP packets traceroute sends by default.[x]
The time-to-live (TTL) value, too known as hop limit, is used in determining the intermediate routers being traversed towards the destination. Traceroute sends packets with TTL values that gradually increase from packet to packet, starting with TTL value of one. Routers decrement TTL values of packets by one when routing and discard packets whose TTL value has reached nix, returning the ICMP error message ICMP Fourth dimension Exceeded.[9] For the first set of packets, the get-go router receives the packet, decrements the TTL value and drops the package considering it then has TTL value zero. The router sends an ICMP Time Exceeded message back to the source. The next set up of packets are given a TTL value of two, so the first router forrad the packets, but the second router drops them and replies with ICMP Fourth dimension Exceeded. Proceeding in this way, traceroute uses the returned ICMP Fourth dimension Exceeded letters to build a list of routers that packets traverse, until the destination is reached and returns an ICMP Destination Unreachable message if UDP packets are being used or an ICMP Repeat Reply message if ICMP Echo messages are existence used.[9]
The timestamp values returned for each router along the path are the delay (latency) values, typically measured in milliseconds for each parcel.
The sender expects a reply within a specified number of seconds. If a parcel is not acknowledged within the expected interval, an asterisk is displayed. The Internet Protocol does non require packets to accept the same road towards a particular destination, thus hosts listed might be hosts that other packets have traversed. If the host at hop #Due north does non reply, the hop is skipped in the output.
If a network has a firewall and operates both Windows and Unix-like systems, more i protocol must be enabled inbound through the firewall for traceroute to work and receive replies.
Some traceroute implementations use TCP packets, such equally tcptraceroute and layer four traceroute (lft). PathPing is a utility introduced with Windows NT that combines ping and traceroute functionality. MTR is an enhanced version of ICMP traceroute available for Unix-like and Windows systems. The various implementations of traceroute all rely on ICMP Time Exceeded (type 11) packets being sent to the source.
On Linux, tracepath is a utility similar to traceroute, with the primary deviation of not requiring superuser privileges.[11]
Cisco's implementation of traceroute besides uses a sequence of UDP datagrams, each with incrementing TTL values, to an invalid port number at the remote host; past default, UDP port 33434 is used. An extended version of this command (known as the extended traceroute command) tin change the destination port number used by the UDP probe messages.[12]
Usage [edit]

Router addresses can exist superimposed upon maps of their physical locations. This case shows a request from New Zealand to an IP address in Massachusetts which takes a route that passes through Europe.
Most implementations include at to the lowest degree options to specify the number of queries to send per hop, time to wait for a response, the hop limit and port to utilise. Invoking traceroute with no specified options displays the list of bachelor options, while human being traceroute presents more than details, including the displayed fault flags. An example on Linux:
$ traceroute -w three -q 1 -yard 16 instance.com traceroute to example.com (93.184.216.34), xvi hops max, threescore byte packets 1 * ii * ... xv * 16 * In the case above, selected options are to wait for three seconds (instead of five), transport out but one query to each hop (instead of three), limit the maximum number of hops to 16 before giving up (instead of thirty), with example.com as the final host.
Traceroute can be used to help identify incorrect routing table definitions or firewalls that may exist blocking ICMP traffic, or high port UDP in Unix ping, to a site. [ clarify ] A correct traceroute response does not guarantee connectivity for applications every bit a firewall may permit ICMP packets just non allow packets of other protocols.
Traceroute is also used past penetration testers to gather information about network infrastructure and IP accost ranges around a given host.
It can also be used when downloading data, and if there are multiple mirrors available for the same piece of data, each mirror can be traced to get an idea of which mirror would be the fastest to use.
Origins [edit]
The traceroute transmission page states that the original traceroute program was written by Van Jacobson in 1987 from a proffer by Steve Deering, with particularly cogent suggestions or fixes from C. Philip Forest, Tim Seaver and Ken Adelman. The author of the ping programme, Mike Muuss, states on his website that traceroute was written using kernel ICMP support that he had earlier coded to enable raw ICMP sockets when he first wrote the ping programme.[13]
Limitations [edit]
Traceroute limitations[14] are well known and should be taken into business relationship when using the tool. For case, traceroute does not notice paths at the router level, but at the interface level. Another limitation appears when routers practise not respond to probes or when routers accept a limit for ICMP responses.[15] In the presence of traffic load balancing, traceroute may indicate a path that does not really exist; to minimize this problem at that place is a traceroute modification called Paris-traceroute,[sixteen] which maintains the flow identifier of the probes to avoid load balancing.
Run across also [edit]
- Looking Drinking glass server
- netsniff-ng – a Linux networking toolkit with an democratic system traceroute utility
References [edit]
- ^ "Traceroute6(8) - Linux man folio".
- ^ "Tracert6(eight): IPv6 traceroute tool - Linux man page".
- ^ tracert.cpp on GitHub
- ^ – Linux Programmer'due south Manual – Administration and Privileged Commands
- ^ – FreeBSD Organization Manager's Manual
- ^ – NetBSD System Manager's Manual
- ^ – OpenBSD System Manager'southward Manual
- ^ – DragonFly BSD System Maintenance and Operation Commands Transmission
- ^ a b c Comer, Douglas (2004). Computer Network and Internets with Cyberspace Applications. Pearson Education, Inc. pp. 360–362. ISBN978-0131433519.
- ^ "Tracert". Microsoft Docs . Retrieved December eleven, 2020.
- ^ "tracepath(8) – Linux man page". linux.die.net . Retrieved 2015-06-21 .
- ^ "Agreement the Ping and Traceroute Commands". Cisco IOS Software Releases 12.one Mainline. cisco.com. 2006-11-29. Retrieved 2013-12-08 .
- ^ The Story of the PING Program
- ^ Ray Belleville (March 3, 2017). "Limitations of Traceroute Explained".
- ^ Marchetta, P.; Montieri, A.; Persico, Five.; Pescapé, A.; Cunha, Í; Katz-Bassett, E. (June 2016). "How and how much traceroute confuses our understanding of network paths". 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Local and Metropolitan Area Networks (LANMAN): i–7. doi:10.1109/lanman.2016.7548847. ISBN978-1-4673-9882-4. S2CID 4643833.
- ^ "Paris Traceroute". paris-traceroute.net . Retrieved 2017-06-10 .
Further reading [edit]
- Frisch, Æleen (2001). Windows 2000 Commands Pocket Reference. O'Reilly. ISBN978-0-596-00148-iii.
- Stanek, William R. (2008). Windows Command-Line Administrator's Pocket Consultant, 2nd Edition. Microsoft Printing. ISBN978-0735622623.
- Barrett, Daniel J. (2012). Macintosh Final Pocket Guide: Take Command of Your Mac. O'Reilly. ISBN978-1449328986.
External links [edit]
- RFC 1393: Traceroute using an IP Option Internet RFC
- How traceroute works – InetDaemon
- Tracert – Windows XP Command-line reference
Which Command Is Used To Determine The Route A Packet Takes?,
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Traceroute
Posted by: randallhatione.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Command Is Used To Determine The Route A Packet Takes?"
Post a Comment