Which Atx Form Factor Is Essentially No Longer In Use?
Overview Between AT, ATX, Mini-ITX and Other Motherboard Form Factors
Tabular array of Content
- Class Factor Overview
- ATX
- Micro-ATX (mATX)
- Mini-ITX
- BTX
- NLX
- Extended ATX (EATX)
- AT and Infant AT
- XT
- Other Grade Factors
- Form Factor Summary
Form Factor Overview
The motherboard is the main component of a computer. It is the large circuit board where all other components of a estimator connects to - such every bit the CPU, memory modules, hard drives, and graphics card. Motherboards come in a diverseness of dissimilar shapes and sizes, which is known as the form gene. In additional to the dimension, a course factor volition also dictate the layout and specifications of the ports, expansion slots, mounting holes, ability supply, and of motherboard components. In that location have been a variety of form factors over the decades. Nevertheless, simply the ATX form factor is common today. Regardless of the form factor, each has its ain standardized which manufacturers must follow to ensure their parts are compatible with a particular motherboard.
This article will provide an quick overview of today'due south common ATX course cistron, along with some popular from the by.
ATX Class Factor
The ATX is the most common motherboard form factor used today. ATX is an abbreviation for Advanced Technology eXtended. Many consider the ATX blueprint a vast comeback over the previous standard AT form factor which had limitations. Considering it was released in 1995 by Intel, the fact that it is however the standard today is testament that ATX was ahead of its time. and addresses. The ATX was slow to grab on due to the long-time acceptance of the AT grade factor, only it slowly gained popularity. Most motherboards today are ATX and the AT course factor is rarely establish today expect in legacy systems.
Some advanced features of the ATX format:
- Integrated I/O Connectors
While the AT uses headers on the board that are fastened to the actual ports on the dorsum of the case, the ATX board has the actual ports built right onto the board. This makes installation easier and enhances reliability. This includes an integrated PS/2 mouse connector. - Reduced Overlap Betwixt Board and Drives
The ATX lath looks like it is rotated xc degrees and so that it does not overlap the bulldoze bays in the front. This fashion, 1 can achieve the entire board instead of having to reach around a drive, or even remove the bulldoze, in order to achieve sure areas of the motherboard. This too reduces rut. - Reduced Processor Interference with Cards
The processor is moved from the front of the board near the slots to the back, tiptop of the board, near the power supply. This means that a user can install full-length expansion cards in the slot without having to worry about hitting the CPU or heat sink. - User-Friendly Power Connector
ATX uses one twenty-pin connector to attach to the motherboard. The ATX connector is too keyed so that it will only go in the right way. This is easier than the two separate connectors of the AT class which look virtually the same. It also gets rid of the problem of frying the board due to misplacement of the connectors on the motherboard. - Better Cooling Conditions
The ATX power supply blows air into the case instead of out. This means that air blows out all the holes in the case and thus keeps dust out. - 3.3 Volt Power
The ATX motherboard is designed to accept iii.3 volt power directly from the power supply. Since almost all modern processors operate at iii.3 volts, this removes the need for a voltage regulator on the motherboard to reduce the voltage from 5V to 3.3V. It must be noted, though, that many processors don't apply this voltage, and therefore must use a voltage regulator anyway. - Automated Controls
The ATX power supply is capable of being controlled through software and other ways. This is because it e'er has a slight voltage going through it. This gives the computer the ability to turn itself on at specified times and perform some chore given to information technology by the software. Some ATX motherboards have the selection of turning the system on by pressing the space bar on your keyboard or being woken up past a command sent downward through the LAN. Lastly, the shut down process is automated using ATX. When you choose "Shut Downward", the computer volition perform all shut downward tasks, then turn itself off.
Micro-ATX (mATX) Form Factor
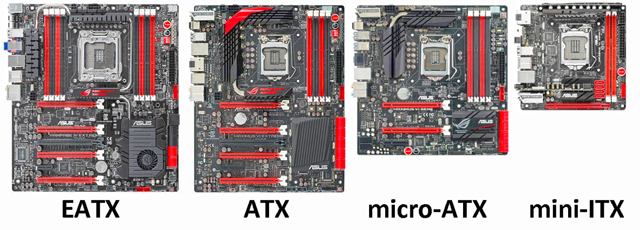
The Micro-ATX (sometimes abbreviated as mATX) motherboards are similar to the ATX board except for its dimension - 9.vi" ten 9.six" versus 12" ten 9.6". Being smaller, mATX form factor boards are platonic for modest figurer chassis. Because of its smaller size, there are fewer expansion and/or memory slots on mATX motherboards.
Despite being smaller, information technology does not mean mATX motherboards are less capable or cheaper than a comparable full size ATX motherboard. The ASUS ROG Maximus XI Gene Z390 mATX motherboard is packed with advanced technologies to satisfy the need of gamers and tin can cost more than many standard size ATX motherboards.

Despite its small size, mATX tin can yet be fully loaded with advanced technologies.
![]()
Mini-ITX Grade Gene
Released in 2001 and developed by VIA Technologies, the Mini-ITX is fifty-fifty smaller in size (at 6.vii" x 6.7") to the Micro-ATX. It was designed to accommodate the growing trend of making computers smaller in size. Because it is much smaller, this form cistron is typically not platonic for some computer enthusiast every bit at that place is usually just one expansion slot and two memory slots, thus limiting upgrade and add-on options. Yet, existence smaller, Mini-ITX motherboards consumes less power and typically does not require a large cooling component.
Mini-ITX boards are compatible with ATX and Micro-ATX computer cases as the mounting points and back console are located in the aforementioned position on the circuit board. Variants to the ITX form cistron after emerged that includes the Nano-ITX in 2003, the Mobile-ITX in 2007, and the Pico-ITX also in 2007. All are designed for low-cost, low-profile computers and devices.
BTX Form Cistron
The BTX form factor was released by Intel 2004 as a replacement to ATX that incorporates feature such as a new layout pattern to allow for better airflow and newer technologies to conform higher power consumption. BTX (an abridgement for Balanced Technology eXtended) form format was non widely adopted despite the benefits it offer. This was primarily due to the increase in more than energy-efficient components such as CPUs and GPUs. These effectively negated the master benefits BTX offered.
The original BTX specification was uniform with ATX estimator cases and power supplies. However, the specification was later changed and it required BTX-compatible cases and power supply unit. Despite its benefits, BTX was not wide adopted and in 2006, Intel announced it was discontinuing development of BTX.
NLX Form Factor
The NLX (an abridgement for New Low Contour eXtended) grade factor was created by Intel for depression-toll and low-profile computers in the late 1990'due south. Considering computers with NLX motherboards are slim, a riser board is used to accommodate expansion cards in such a tight space. It does this by allowing addition cards to be seated parallel to the motherboard instead of perpendicular to it as with ATX for mATX boards.
NLX was not widely adopted and was superseded by the Micro-ATX and Mini-ITX class factors.
Extended ATX (EATX) Form Factor
The EATX (an abbreviation for Extended ATX) is a variant of the ATX grade factor. This standard defines a larger motherboard excursion board. As a outcome, more than expansion slots can be accommodated (such equally 8 instead of 4 on an ATX) along with more retention slots. These motherboards aren't commonly found on consumer motherboards but more on servers.
AT and Babe-AT Form Factors
The AT course factor was developed by IBM and was the common form factor of the 1980s. AT is an abbreviation for Advanced Technology and this form factor comes in 2 flavors - AT (sometimes referred to as Full-AT) and Baby AT. The two basically differ in size. An AT motherboard is about 12" x 13.eight" which means information technology tin't fit in many of today's cases. AT form factor motherboards were used for the Intel 80386 or earlier processors and was the dominated course cistron in the 1980s. Despite its popularity, information technology did take its drawbacks. For computer technicians, working inside a calculator case with an AT board was troublesome as its large size was oftentimes overlapped past the drive bays making installation and access to various connectors difficult. The AT is the oldest and largest form factor until the introduction of Babe-AT.
Baby AT was the form used by many boards and cases at the time. Many Socket seven and Pentium-class boards employ this form cistron. A Baby AT board is approximately 8.5" broad and 13" long. The size varies a little from board to board. This reduced size made it easier to work within the example only considering at that place is more room. There are 3 rows of mounting holes to hold the board in the case.
AT course boards share common traits. They all have serial and parallel ports (no longer mutual today) attached to the case in an expansion slot and connected to the board through cables. They as well take a unmarried keyboard connector soldered onto the board at the back of the board. The processor is all the same at the front of the board and tin sometimes arrive the way of expansion cards. The SIMM slots (memory slots) are in different places, although they are nigh always at the pinnacle of the lath.
There are some annoyances with the AT blueprint that eventually emerged since its introduction. One was due to the layout. Since all input ports are attached to the instance and and then connected to the motherboard via a cable, the board must have connectors for all of them - such as: COM ane, COM 2, printer port, USB, and PS/2 mouse. Often these connectors are directly next to the IDE channel connectors (for difficult drives) and floppy drive connector. This leads to a severe cramping problem and makes working inside the computer more than difficult.
Additionally, the AT design is non conducive to efficient cooling of the organisation. Air is not blown over the areas that demand it, namely the CPU. Also, the air flow draws in dust. Over fourth dimension, the AT power supply will go dusty and the inside of the system will be coated with a layer of grit. For this reason, information technology was recommended that the computer case was to be removed regularly blow off the interior of the example.
The AT form factor was retired when ATX was introduced past Intel in 1995.
XT Form Factor
The XT (an abbreviation for eXtended Technology) was the beginning grade factor introduced in 1983 by the then popular IBM Personal Computer XT, or simply IBM XT.
The IBM XT was intended for business organization users and can toll upwards $3,000 USD and more at the fourth dimension, or nearly $7,800+ USD in 2019 afterwards factoring in inflation. Additionally, the XT weighed approximately 32 pounds.
Other Form Factor
The form factors listed is not all encompassing. Described here are the standards that are/were popular or worth noting. There are many other form factors developed over the past decades that are not included such as Flex ATX, LPX, Mini-LPX, DTX, WTX, and ETX to proper noun a few.
Form Cistron Summary
| ATX | EATX | BTX | Micro-ATX | Mini-ITX | Nano-ITX | Pico-ITX | Mobile-ITX | NLX | AT | Baby AT | XT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimension* | 12 ten 9.6" | 12 x 13" | 12.8 ten 10.five" | nine.half-dozen ten 9.6" | 6.7 x 6.7" | 4.vii ten 4.7" | 2.8 x 3.nine" | 2.4 10 2.4" | 8 x x" | 12 x 13.8" | 8.5x 10" | 8.5 ten xi" |
| Power Connection | 20- or 24-pin connector | 24-pin connector | 24-pin connector | 24-pivot connector | 4-pin, 24-pivot connector, or DC jack | 20-pin connector | Ii 6-pin connectors | |||||
| Expansion Slots | Many | Many | Few | Few | Few | 1 | 0 | 0 | Limited | Many | Many | Many |
| Released Date** | 1995 past Intel | 2004 by Intel | 1996 | 2001 by VIA | 2003 by VIA | 2007 past VIA | 2007 by VIA | 1999 by Intel | 1984 by IBM | 1985 by IBM | 1983 by IBM |
* Actual motherboard dimension varies between manufacturers
** Released/introduced
Which Atx Form Factor Is Essentially No Longer In Use?,
Source: https://www.meridianoutpost.com/resources/articles/atx-vs-at-form-factor.php
Posted by: randallhatione.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Atx Form Factor Is Essentially No Longer In Use?"
Post a Comment